
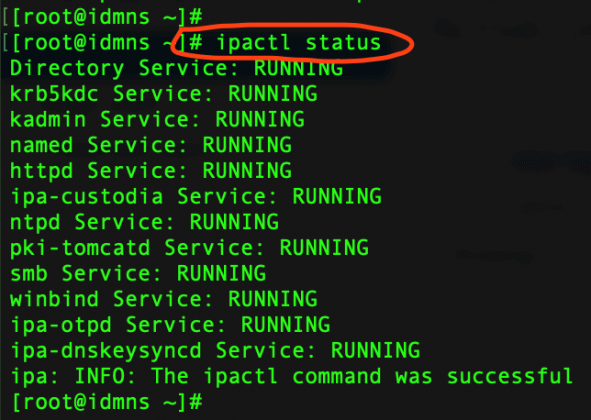
You cannot mix units a value of '3h30m' will result in an error. The value for lifetime must be followed immediately by one of the following delimiters:

Such a error says that the server is not reachable. Kinit: krb5_get_init_creds: unable to reach any KDC in realm EXAMPLE.COM There are many possible reason why you can't get a ticket. Troubleshooting # Note: The realm name is Case-sensitive and is usually UPPERCASE. Kinit -p you get no errors You can verify that you have correctly obtained a ticket using the klist tool. Any valid Kerberos Principal (AD User) can be substituted for "Administrator". To test the operation of Kerberos, request a Ticket Granting Ticket ( TGT) with the Kinit command, as shown below.
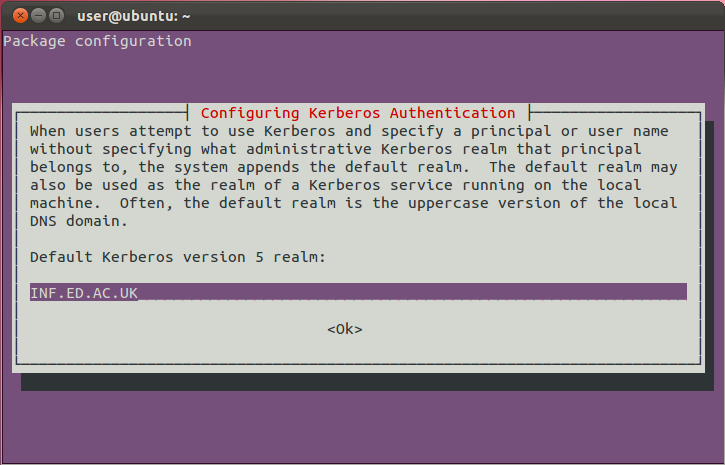
A keytab used with kinit can be thought of as storing a password in a file.The kinit command obtains or renews a Kerberos ticket-granting ticket from the Key Distribution Center options specified in the /etc/ nf file or DNS SRV records if you do not specify these options on the command-line. So after you use the keytab for kinit, you have a kerberos ticket of the principal in the keytab. Both ultimately use the same secret key to decrypt the ticket. As far as the kerberos protocol is concerned there really is no difference between using a keytab to kinit and using a password. So when you kinit using a keytab, it uses the key in the keytab to decrypt the blob. A keytab is just means for storing the secret key in a local file. Password to the secret key used by the KDC. When you kinit with a password, kerberos uses a "string to key" algorithm to convert your If you know your secret key, you can unencrypt the blob and use that to access other services. When you kinit what is going on under the covers is that you are asking the KDC for a ticket to ask for more kerberos tickets, it encrypts that ticket with your secret key. The kerberos KDC does not store your password, but a secret key. This is glossing over many important details, but basically all you ever get from the KDC is an encrypted blob.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
